Fine-Grained Access Management
Fine-Grained Access Management is an optional feature for managing access to your SpiceDB Permissions Systems deployed with SpiceDB Dedicated and SpiceDB Enterprise. Those familiar with configuring IAM on any major cloud provider should feel comfortable with the basic concepts:
- Service Accounts represent workloads (e.g., an application calling the SpiceDB API)
- Tokens identify Service Accounts.
- Permissions map to SpiceDB API calls, an optional FGAM Caveat defined as a CEL expression, and are associated with a Role.
- Roles define a collection of Permissions.
- Policies bind a Service Account to a Role
Concepts
Service Accounts
Service Accounts represent your workloads. We recommend creating a Service Account for each application that will access the SpiceDB API.
A Service Account can have zero or more Tokens.
Tokens
Tokens are long-lived credentials that identify the Service Account. SpiceDB clients must provide a Token in the Authorization header of an API request to perform actions granted to the Service Account through Roles bound by Policies.
Roles and Permissions
Roles are lists of Permissions for accessing the SpiceDB API. You grant Roles to zero or more Service Accounts via Policies.
Each Permission specifies an API call and an optional CEL expression, which is evaluated at runtime to determine whether or not to grant the Permission.
Adding the Permission to a Role means each Service Account assigned the Role will have the corresponding API access. Calling the API method will only be authorized if a Service Account has been granted direct access via a Role and a Policy binding it.
Advanced Roles with Conditions
Fine-Grained Access Management offers advanced Permissions by letting users define dynamic conditions that must be met at request time for the request to be authorized. This is achieved by augmenting fine-grained Permissions with Google's CEL expressions language.
Each Permission provides an input text box to introduce an optional conditional expression. When included, an API request will be authorized if:
- the Service Account has been granted a Permission
- the expression of the Permission is met
SpiceDB Dedicated will expose the protobuf payload to the expression language, so the following variables are available in the expression:
WriteRelationshipsRequestReadRelationshipsRequestDeleteRelationshipsRequestWriteSchemaRequestReadSchemaRequestCheckPermissionRequestLookupResourcesRequestLookupSubjectsRequestExpandPermissionTreeRequestWatchRequest
This lets you extend the logic to authorize an API request beyond "granted / not granted". Here are a few examples:
| Example | Expression |
|---|---|
| Grants Permissions to update only a specific type of resource on a write request | WriteRelationshipsRequest.updates.all(x, x.relationship.resource.object_type == "resource") |
| Grants Permission to update only a specific type of subject on a write request | WriteRelationshipsRequest.updates.all(x, x.relationship.subject.object.object_type == "user") |
| Allows only write operations that use CREATE | WriteRelationshipsRequest.updates.all(x, x.operation == authzed.api.v1.RelationshipUpdate.Operation.OPERATION_CREATE) |
| Allows reading only relationships of a specific type of resource type | ReadRelationshipsRequest.relationship_filter.resource_type == "resource" |
| Blocks writing the schema that contain specific strings | !WriteSchemaRequest.schema.contains("blockchain") |
| Only allows checking a specific Permission | CheckPermissionRequest.permission != "admin" |
| Only allows looking up resources after a specific Permission | LookupResourcesRequest.permission != "admin" |
Any Public API type will be available to the CEL expression so that you can traverse any type and its fields using language operators. For more details on CEL's language definition, please refer to CEL language specification.
Policy
Policies bind Roles to Service Accounts. Each Policy represents a 1:1 mapping of a Service Account to Role. Binding multiple Roles to a single Service Account is additive, so if any of the Roles have a Permission, then that Service Account receives that Permission.
Example: Assign a read-only Role to Service Account
Pre-Requisites
Let's illustrate how you can create a read-only Role for your Service Account.
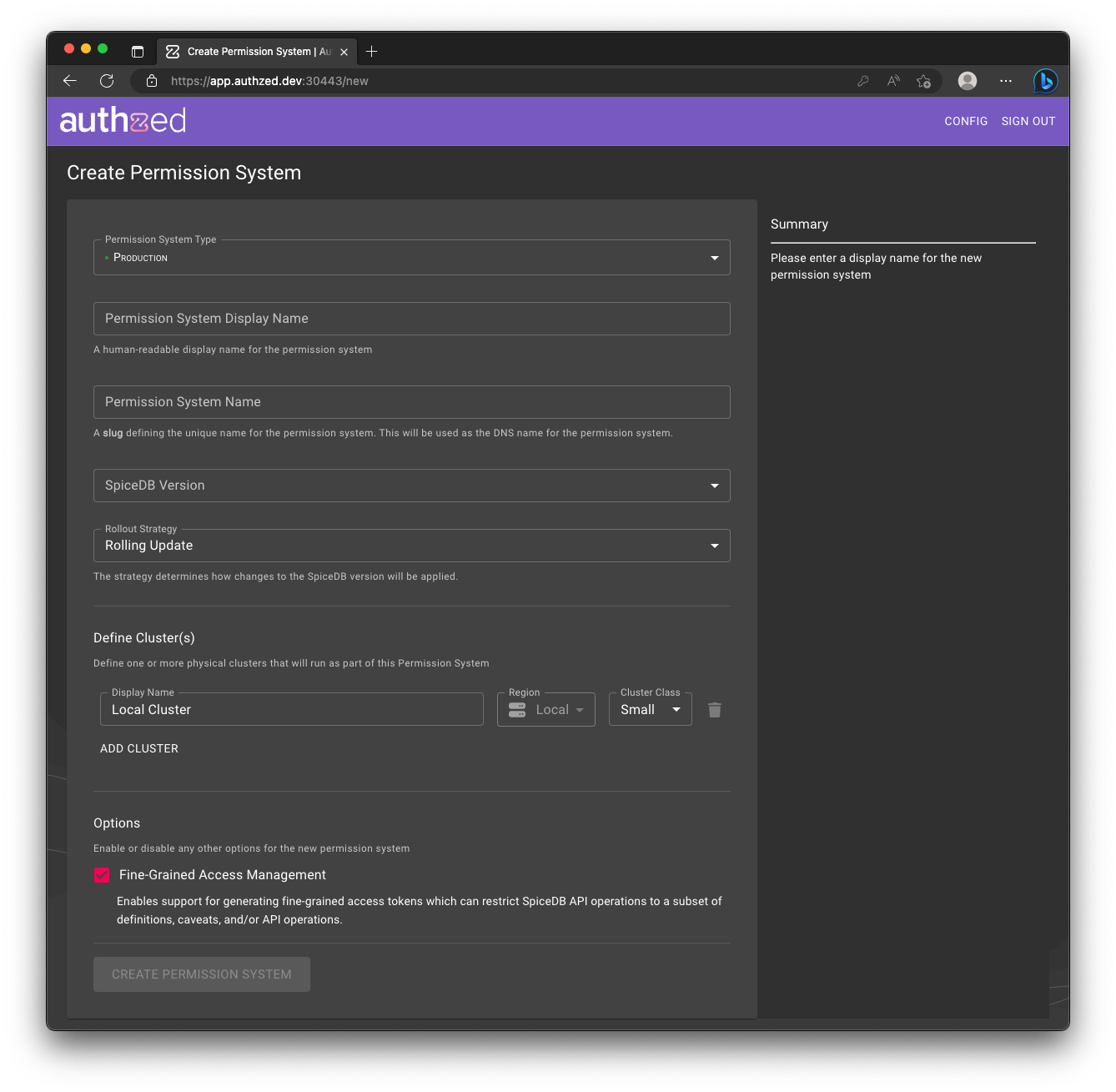
Start by ensuring your Permissions System has enabled Fine-Grained Access Management. You can do this by enabling the corresponding option while creating a Permissions System.
Create a Service Account
Once you have a Permissions System, click Access Management from the left navigation area. Now you will see a list of empty Service Accounts. Create a Service Account by hitting Create Service Account, and providing a Display Name and Description.
Now you’ll see the information page, with the global ID of the Service Account, and the date and time of creation.
Go back to see the Service Account page, which now lists the new Service. To remove the Service, use the bin icon on the right side of the entry.
Create a Role
Next, let's go ahead and create a Role that only has access to read-only operations on your Permissions System.
Hit Create Role, and provide a Display Name and Description.
In the API Permissions, dropdown, you can choose from all of SpiceDB's APIs.
To add a Permission to your Role, hit Add API Permission.
When you're done, you'll see a list of Permissions currently associated with the Role.
Leave the Optional Expression empty for now.
Now go back to the Role page, and you'll see your new read-only Role listed. To remove the Role, use the bin icon on the right side of the entry.
You can now grant the Role to any Service Account by binding them with a Policy.
Create a Policy
Head to the Policy page, which gives you an overview of all existing Policies.
Hit Create Policy, and select the Principal and Assigned Role. Choose the Service Account you created above and hit Create Policy.
Create a Token
The last step is to issue a Token for your Service Account. ⚠️ These are long-lived, so adequate secret management is warranted.
Head to Access Management > Service Accounts and choose your Service Account.
Hit Tokens from the left navigation menu on the Service Account page. Click Create Token.
That's it! You can now make restricted calls from your workload to your SpiceDB Permissions System.